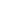
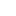
Clay Seals from First Temple Period Discovered in Jerusalem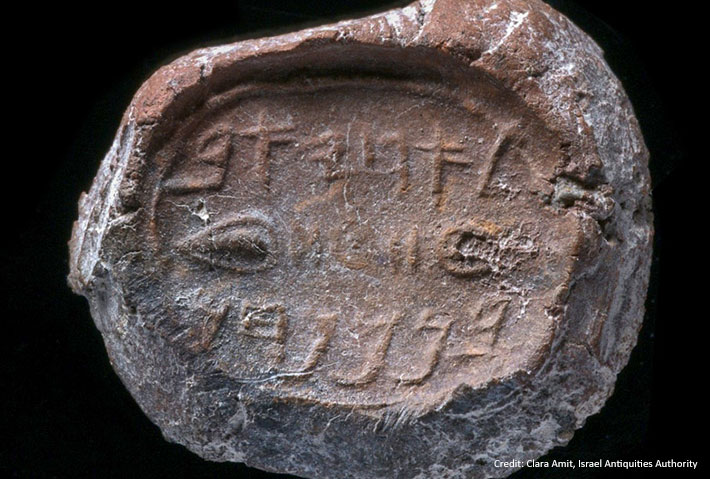
Researchers say this discovery offers a compelling case that Jerusalem played an important role in the Judean kingdom.During recent excavations in Jerusalem’s Old City, archaeologists discovered a small collection of clay seals used to secure letters or documents during the Iron Age. Researchers say this discovery offers a compelling case that Jerusalem played an important role in the Judean kingdom. This from Haaretz:
The seals will be on display this week at the annual City of David archaeology conference. Researchers say this discovery offers a compelling case that Jerusalem played an important role in the Judean kingdom. |
|
|